Operators
in C Part 1 :
As discussed in our previous posts ,individual
constants , variables can be joined by various operators to form expressions .
C includes a number of operators as follows :
· Arithmetic
operators
· Unary
operators
· Relational
and Logical operators
· Assignment
operators
· Conditional
operators
· Bitwise
operators
The data item that operator act upon are called
operands. Some operands requires two operators while others act upon only one
operand.
Arithmetic Operators:
Below are the arithmetic operators and their purpose.
OPERATOR
|
PURPOSE
|
+
|
Addition
|
-
|
Subtraction
|
*
|
Multiplication
|
/
|
It
takes quotient after division
|
%
|
It
takes remainder after division
|
Examples:
If a and b are two integer variables and there
values are 10 and 3 ,then
EXPRESSION
|
VALUE
|
a
+ b
|
13
|
a
– b
|
7
|
a
* b
|
30
|
a
/ b
|
3
|
a
% b
|
1
|
If c and d are two floating point variables and
there values are 12.5 and 2.0
c
+ d
|
14.5
|
c
- d
|
10.5
|
c
* d
|
25.0
|
c
/ d
|
6.25
|
c
% d
|
Not
possible
|
Note: the
modulo (%) operator requires both the operands to be integer and the second
operand to be non zero.
If e and f are two character variables that
represents the values for e and f as P
and T , then
e
|
80
|
e
+ f
|
164
|
e
+ f + 5
|
169
|
e
+ f +’5’
|
217
|
Unary operators :
Unary operators are a class of operators that acts
upon single operand to produce a new value.
The common unary operators are :
OPERATOR
|
What is it
|
-
|
Unary
minus
|
++
|
Increment
operator
|
--
|
Decrement
operator
|
sizeof
|
Size
of the operand
|
Example of unary minus :
If a=-4 , b=5 and c=-6 and a=-a , b=-b ,c =-c then
,the values of a , b and c would be 4, -5 and 6 respectively.
A ++ operator increments the value of the operand by
1(i.e , adding the value of operand by one).
If the operator precedes the operand (e.g, i++) then
,the operand will change its value before it is utilized for the intended
purpose with in the program. The operators are called pre increment operators.
If the operator follows the operand (e.g.i++),then
the value of the operand is altered after it is utilized. It is called as post
increment operator.
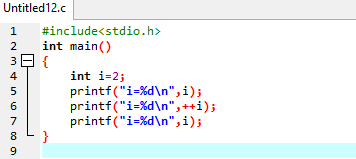
Example program for pre increment operator :
Output:
Example program for post increment operator:
Output:
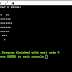
Example program for size of operator:
Output:
Note : The size of operator returns the size in bytes taken by each data type to store its value. The size changes depends on the compiler.
The associativity of the unary operator is from
right to left.
For example :
If x and y are integer variables whose values are 10
and 20. The value of the expression –x+y
will be -10+20=10.
The unary minus operation is carried out before the
addition operation.
Using the same expression if parenthesis are used ,
so the expression becomes –(10+20)= -30.
The addition now precedes the unary minus operation.
Lets continue operators in C in our next post .
Thank you..
for more posts on c programming : https://iamafutureprogrammer.blogspot.com






![Java Code 3 _ Two - digit " Reduced Subtracted Form " [Wipro Interview Question]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjfknAUiMwSb6Ma-V3Usa9M-80j4etXJF3-Ns2u_azXAb33KPwfsvZtP17a2Tu1aLYKhCOmcG5ivzogedb8cXJzdE-Qd_q5VKx_VthmzjgrnnTYD0VYXoBSId6fvfoqTTXf2JRF_wij0Rw/w72-h72-p-k-no-nu/Screenshot+%252819%2529.png)


